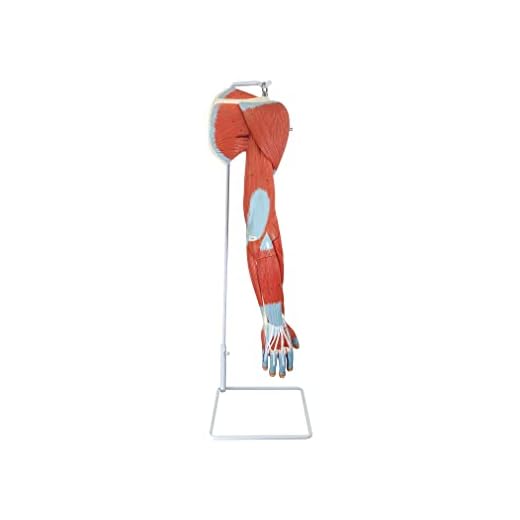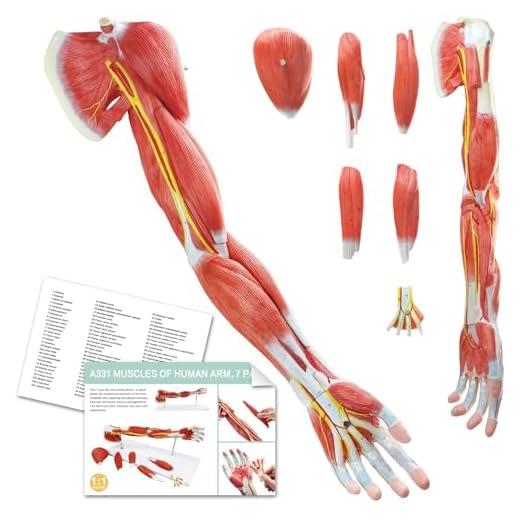

The human arm is a remarkable complex structure that allows us to perform a wide range of movements and tasks. It is composed of several bones, muscles, and joints that work together to provide us with strength, flexibility, and dexterity. One of the key features of the arm is its ability to move along different axes, enabling us to perform various types of movements.
When it comes to axes, the human arm can be divided into three main categories: the anteroposterior axis, the superoinferior axis, and the longitudinal axis. These axes represent the three-dimensional space in which the arm can move. Each axis allows for different types of movements and is essential in our everyday activities.
The anteroposterior axis, also known as the flexion-extension axis, runs from front to back. It allows us to perform flexion and extension movements, such as bending and straightening the elbow. This axis is responsible for the forward and backward movement of the arm and is crucial in activities like throwing, punching, and lifting.
The superoinferior axis, also known as the abduction-adduction axis, runs from top to bottom. It allows us to perform abduction and adduction movements, such as raising and lowering the arm. This axis is responsible for the up and down movement of the arm and is essential in activities like reaching overhead or to the side.
The longitudinal axis, also known as the rotation axis, runs from the shoulder to the wrist. It allows us to perform rotational movements, such as pronation and supination of the forearm. This axis is responsible for the twisting movement of the arm and plays a crucial role in activities like turning a doorknob or using a screwdriver.
In summary, the human arm has three main axes that enable us to perform a wide range of movements. These axes, the anteroposterior axis, the superoinferior axis, and the longitudinal axis, allow us to flex and extend, raise and lower, and rotate our arm, respectively. Understanding the different axes of the human arm can help us appreciate the complexity and versatility of this vital part of our body.
Understanding the Human Arm Anatomy
The human arm is a complex structure that allows us to perform various movements and tasks. It consists of several bones, joints, muscles, and ligaments, all working together to provide functionality and flexibility. The arm is divided into three main sections: the upper arm, the forearm, and the hand.
Upper Arm
The upper arm is the region between the shoulder and the elbow. It consists of a single bone called the humerus, which is the longest bone in the arm. The humerus connects the shoulder joint to the elbow joint and provides stability and support for arm movements. The upper arm also contains a network of muscles, including the biceps and triceps, which help in flexing and extending the elbow joint.
Forearm
The forearm is the region between the elbow and the wrist. It consists of two bones called the radius and the ulna. The radius is located on the thumb side of the forearm, while the ulna is on the pinky side. These bones work together to allow rotational movements of the forearm, such as twisting the hand. The forearm also contains muscles, tendons, and ligaments that enable movement of the wrist and fingers.
The forearm is responsible for actions such as flexion, extension, pronation, and supination. Flexion and extension refer to bending and straightening movements of the wrist and fingers, while pronation and supination involve rotating the forearm to turn the palm downwards or upwards.
Hand
The hand is the distal part of the arm and is composed of the wrist, palm, and fingers. It consists of multiple small bones called carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges. The wrist is formed by a group of eight carpal bones, which provide stability and flexibility to the hand. The palm consists of five metacarpal bones, one for each finger, and the phalanges are the bones of the fingers.
The hand is responsible for fine motor skills and intricate movements. It allows us to grasp objects, perform delicate tasks, and have a strong grip. The fingers are controlled by a complex network of tendons and muscles, which provide precision and dexterity in various activities.
| Section | Bones | Key Movements |
|---|---|---|
| Upper Arm | Humerus | Flexion, Extension |
| Forearm | Radius, Ulna | Pronation, Supination |
| Hand | Carpals, Metacarpals, Phalanges | Grasping, Fine Motor Skills |
An Overview of the Human Arm Structure
The human arm is a complex structure that allows for a wide range of movements and functions. It consists of several components, including bones, muscles, joints, and nerves, all working together to perform various tasks.
Bones
The arm is made up of three main bones: the humerus, ulna, and radius. The humerus is the longest bone in the arm, running from the shoulder to the elbow. The ulna and radius are located in the forearm, with the ulna on the inner side and the radius on the outer side.
Muscles
The arm is home to many muscles that enable movement and strength. These muscles can be divided into two main groups: the flexors and the extensors. The flexor muscles, located on the palm side of the forearm, allow for flexion of the wrist and fingers. The extensor muscles, located on the back of the forearm, allow for extension of the wrist and fingers.
Additionally, there are muscles responsible for the movements of the shoulder and upper arm, such as the deltoid and biceps brachii muscles. These muscles provide stability and power to the arm during various activities.
Joints
The arm has several important joints that allow for movement and flexibility. The main joints in the arm include the shoulder joint, elbow joint, and wrist joint. The shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint that allows for a wide range of motion, including rotation and abduction. The elbow joint is a hinge joint that enables flexion and extension of the forearm. The wrist joint is a complex joint that enables various movements, such as flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction.
These joints work together to provide stability and mobility to the arm, allowing for a wide range of activities, from everyday tasks to sports and fine motor skills.
Overall, the human arm is a remarkable structure that showcases the intricate interplay between bones, muscles, joints, and nerves. Its complexity and versatility enable us to perform countless tasks and activities, making it an essential part of our daily lives.
The Function of Multiple Axes in the Human Arm
The human arm is a complex structure that enables a wide range of movements and functions. One of the key features of the arm is the presence of multiple axes, which allow for different types of movement.
The arm consists of three main axes: the sagittal, frontal, and transverse axes. Each axis plays a crucial role in facilitating specific movements and functions.
The sagittal axis runs parallel to the midline of the body and allows for flexion and extension movements. This axis is responsible for movements such as bending and straightening the arm. It enables actions such as raising the arm to reach for objects or lowering it to touch the ground.
The frontal axis is perpendicular to the sagittal axis and runs from side to side. It enables abduction and adduction movements, which involve moving the arm away from or towards the body. This axis allows for actions like spreading the arms wide or bringing them close together.
The transverse axis is perpendicular to both the sagittal and frontal axes and runs from top to bottom. It enables rotational movements, such as pronation and supination. Pronation involves the rotation of the forearm to face the palm downwards, while supination rotates the forearm to face the palm upwards. These movements are essential for activities like pouring a drink or turning a doorknob.
The presence of multiple axes in the arm allows for a greater range of motion and functionality. It enables us to perform various tasks, from simple actions like picking up objects to complex movements involved in sports or artistic activities.
| Axis | Movement | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Sagittal | Flexion/Extension | Bending and straightening the arm |
| Frontal | Abduction/Adduction | Spreading the arms wide or bringing them close together |
| Transverse | Pronation/Supination | Pouring a drink or turning a doorknob |
The Importance of the Shoulder Joint
The shoulder joint is one of the most important joints in the human body. It plays a critical role in enabling a wide range of movements and allows us to perform everyday tasks with ease.
The shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint, connecting the upper arm bone (humerus) to the shoulder blade (scapula). This unique structure allows for a remarkable degree of flexibility and mobility, making it possible for us to reach, lift, and rotate our arms in various directions.
Some of the key functions of the shoulder joint include:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Flexion | Allows us to lift our arms forward and upwards. |
| Extension | Allows us to move our arms backward. |
| Abduction | Enables us to move our arms away from the body. |
| Adduction | Allows us to bring our arms back towards the body. |
| Rotation | Enables us to rotate our arms internally and externally. |
| Circumduction | Allows us to move our arms in a circular motion. |
As you can see, the shoulder joint is involved in a wide range of movements, making it crucial for activities such as reaching, throwing, lifting, and even simple tasks like combing our hair or putting on clothes.
However, due to its high mobility, the shoulder joint is also susceptible to injuries and conditions such as dislocations, fractures, arthritis, and rotator cuff tears. It is important to take care of our shoulders by maintaining proper posture, practicing regular exercise to strengthen the supporting muscles, and seeking medical attention if any pain or discomfort persists.
In conclusion, the shoulder joint is not only a remarkable anatomical structure but also a vital component of our daily lives. Understanding its importance and taking appropriate care can help us maintain optimal shoulder health and enjoy a wide range of movements throughout our lives.
The Elbow Joint and Its Role in Arm Movement
The elbow joint is one of the most important joints in the human arm. Located between the upper and lower arm, it allows for a wide range of movement and plays a crucial role in everyday activities.
Composed of three main bones – the humerus, radius, and ulna – the elbow joint acts as a hinge, enabling the arm to bend and straighten. This flexion and extension movement is essential for performing tasks such as lifting objects, eating, and writing.
In addition to flexion and extension, the elbow joint also allows for a limited degree of rotation, known as pronation and supination. Pronation refers to the rotation of the forearm and hand inwards, while supination involves the rotation outwards. These movements are crucial for tasks that require gripping and turning, such as opening a door or using a screwdriver.
The elbow joint is supported by strong ligaments and muscles, which help stabilize and control its movements. Muscles such as the biceps and triceps brachii play a significant role in flexion and extension, while the pronator teres and supinator muscles are responsible for pronation and supination.
Overall, the elbow joint is a vital component of the human arm, allowing for a wide range of movements that are essential for performing daily tasks. Its flexibility and stability make it an important joint to maintain and protect through proper exercise and care.
The Wrist and Hand: Complex System for Precise Movements
The human arm is an incredible mechanism that allows us to perform a wide range of tasks. One essential component of this system is the wrist and hand, which enable us to grip and manipulate objects with precision.
Anatomy of the Wrist
The wrist is made up of eight small bones called carpal bones. These bones are arranged in two rows, with the proximal row connecting to the forearm and the distal row connecting to the hand. The carpal bones provide stability and support to the wrist joint, allowing for a smooth range of motion.
The carpal bones are connected to the forearm bones, known as the radius and ulna, by a complex network of ligaments, tendons, and muscles. This intricate arrangement allows for the coordinated movement of the wrist and hand.
Movement of the Hand
Within the wrist, there are several joints that enable movement. The main joints are the radiocarpal joint and the midcarpal joint. These joints allow for flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, and circumduction of the hand.
The hand itself consists of five metacarpal bones connected to the carpal bones. Each metacarpal bone connects to a finger through a joint called the metacarpophalangeal joint. This joint allows for flexion, extension, adduction, and abduction of the fingers.
The fingers are made up of three phalanges, except for the thumb, which has two. These phalanges are connected by interphalangeal joints, which allow for flexion and extension of the fingers.
The complex arrangement of bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, and muscles in the wrist and hand allows for precise movements, such as gripping, grasping, and manipulating objects. This intricate system is vital for everyday activities and is a testament to the incredible capabilities of the human arm.