


Table saw blades are an essential tool for any woodworker. They come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and materials, each designed for a specific purpose. Understanding the differences between these blades can help you achieve the best results in your woodworking projects.
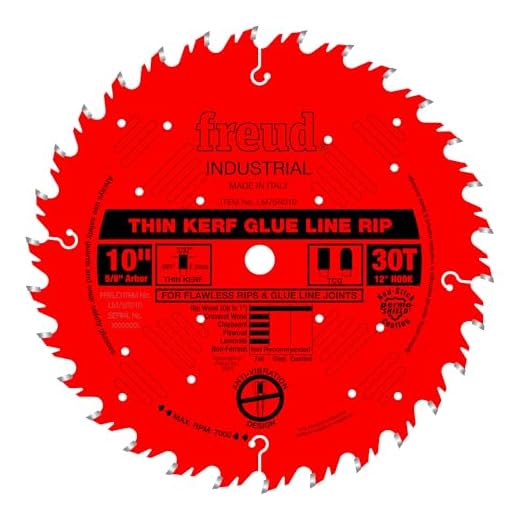
There are three main types of table saw blades: rip blades, crosscut blades, and combination blades. Rip blades are designed to cut along the grain of the wood, making them ideal for making straight cuts with the wood’s natural grain. They have fewer teeth per inch and larger gullets to remove more material quickly.
Crosscut blades, on the other hand, are designed to cut across the grain of the wood. They have more teeth per inch and smaller gullets, which allows for cleaner and smoother cuts. These blades are ideal for making precise and accurate cuts, such as cutting plywood or making miters.
Lastly, combination blades are a hybrid between rip blades and crosscut blades. They are perfect for general-purpose cutting tasks, as they can handle both rip cuts and crosscuts. Combination blades have a moderate number of teeth per inch and medium-sized gullets.
When choosing a table saw blade, there are a few factors to consider: the type of wood you’ll be cutting, the type of cut you want to achieve, and the quality of the blade. High-quality blades will have sharp, carbide-tipped teeth that stay sharp for longer periods. They will also have a level of durability and precision that cheaper blades may lack. Additionally, consider the size and power of your table saw, as not all blades are compatible with every saw.
In conclusion, understanding the difference between table saw blades is crucial for achieving the best results in your woodworking projects. Whether you need to make rip cuts, crosscuts, or a combination of both, choosing the right blade for the job is essential. Invest in high-quality blades to ensure clean, precise, and efficient cuts every time.
Understanding Table Saw Blades: Exploring the Key Differences
Table saw blades come in a variety of styles and configurations, each designed for specific cutting tasks. Understanding the key differences between these blades is essential for achieving the best results in your woodworking projects. This article will explore the main types of table saw blades and discuss how they differ from one another.
1. Rip Blades:
Rip blades are designed for making rip cuts, which involve cutting along the length of the wood grain. These blades typically have fewer teeth with deeper gullets, allowing for faster and more efficient material removal. They produce rougher cuts but are ideal for tasks such as dimensioning lumber.
2. Crosscut Blades:
Crosscut blades are specialized for making crosscuts that go against the wood grain. They have more teeth, with a higher tooth count, and smaller gullets. This configuration allows for smoother and cleaner cuts across the fibers of the wood. Crosscut blades are commonly used for finish carpentry and making precision cuts.
3. Combination Blades:
Combination blades are a versatile option that combines the features of rip and crosscut blades. They have a medium tooth count and are designed to handle both ripping and crosscutting tasks effectively. This makes them a popular choice for general woodworking projects where a variety of cuts may be required.
4. Dado Blades:
Dado blades are unique in that they are designed specifically for making dado, rabbet, and groove cuts. They consist of two outer circular blades and several chippers that fit in between. This configuration allows for adjustable-width cuts, making them suitable for tasks such as joinery and creating strong joints.
5. Specialty Blades:
Specialty blades include a wide range of options designed for specific cutting needs. These blades are tailored for tasks such as cutting melamine, laminate, hardwood, plywood, and non-ferrous metals. They often have unique tooth geometries, coatings, or materials to handle the specific demands of these materials.
When selecting a table saw blade, consider the type of cuts you’ll be making and the materials you’ll be working with. Choosing the right blade for the job will greatly impact the quality of your cuts and the overall success of your woodworking projects. Consult the manufacturer’s recommendations and consult with experienced woodworkers for additional guidance if needed.
Remember: It’s important to select a table saw blade that is compatible with your table saw’s arbor size and rotation direction. Always follow proper safety procedures when handling and installing table saw blades.
Blade Material Matters: Steel vs. Carbide
When it comes to table saw blades, the material used to make the blade can have a significant impact on its performance and durability. Two common blade materials used in table saw blades are steel and carbide. Each material has its own unique characteristics and advantages.
Steel blades are typically made from a high-quality steel alloy. They are known for their durability and strength, making them suitable for heavy-duty cutting tasks. Steel blades can handle a wide range of materials, including wood, plastic, and non-ferrous metals. However, they may not perform as well when cutting harder materials, such as hardwoods or laminates.
On the other hand, carbide blades feature teeth that are tipped with carbide inserts. These inserts are made from a combination of tungsten carbide particles and a metal binder. Carbide blades are known for their superior cutting performance and longevity. They can handle demanding cutting tasks, including cutting hard and abrasive materials, with ease. Carbide blades also tend to stay sharper for a longer period, reducing the need for frequent blade changes.
One of the main advantages of carbide blades over steel blades is their ability to withstand high heat generated during cutting. The carbide inserts dissipate heat more effectively, preventing the blade from overheating and causing damage to the blade or the material being cut. This heat resistance also helps to prolong the life of the blade.
However, carbide blades are generally more expensive than steel blades. This higher cost can be justified by their enhanced performance and longer lifespan. If you frequently work with harder materials or require precise, clean cuts, investing in a carbide blade may be a wise choice.
| Blade Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | Durable and strong, suitable for a wide range of materials | May not perform as well when cutting harder materials |
| Carbide | Superior cutting performance, longer lifespan, heat resistance | Higher cost compared to steel blades |
In conclusion, both steel and carbide blades have their own advantages and disadvantages. The choice between the two ultimately depends on your specific cutting needs and budget. Consider the type of materials you frequently work with and the level of precision and durability required to make an informed decision when selecting a table saw blade.
Teeth Configuration: Ripping Blades vs. Crosscut Blades
When it comes to table saw blades, one crucial aspect to consider is the teeth configuration. Different teeth configurations are designed for specific cutting tasks, such as ripping or crosscutting. Understanding the difference between ripping blades and crosscut blades can help you choose the right blade for your woodworking projects.
Ripping Blades
Ripping blades are designed for making long, straight cuts along the grain of the wood. These blades typically have a low tooth count, ranging from 20 to 30 teeth. The teeth on ripping blades have a large gullet, or the space between the teeth, which helps remove the wood chips efficiently. This configuration allows the blade to quickly remove material and prevent overheating. Ripping blades are most suitable for cutting thicker boards and are optimized for speed rather than smoothness.
Crosscut Blades
Crosscut blades, on the other hand, excel at cutting wood across the grain or at an angle. They have a higher tooth count, typically ranging from 60 to 80 teeth. The teeth on crosscut blades are smaller and have a more complex shape compared to ripping blades. This tooth configuration enables the blade to make clean, smooth cuts. Crosscut blades are ideal for cutting plywood, hardwood, or any material where a clean finish is required.
It’s important to note that while ripping blades and crosscut blades are optimized for specific tasks, there are also combination blades available. Combination blades have a tooth configuration that allows them to handle both ripping and crosscutting to some extent. However, they may not perform as efficiently as dedicated ripping or crosscut blades.
When choosing a table saw blade, consider the type of cuts you will be making most frequently. If you primarily work with thick boards and need to make quick rip cuts, a ripping blade is the way to go. On the other hand, if you prioritize clean, smooth crosscuts, a crosscut blade would be more suitable. If you frequently switch between ripping and crosscutting tasks, a combination blade can offer a versatile solution.
Ultimately, the teeth configuration of a table saw blade plays a significant role in its performance and the quality of the cuts it produces. Understanding the differences between ripping blades and crosscut blades can help you make an informed decision and achieve the best results for your woodworking projects.
Blade Size: Choosing the Right Diameter for Your Needs
When it comes to table saw blades, one important factor to consider is the diameter of the blade. The blade size can greatly affect the performance and versatility of the saw, so it is essential to choose the right diameter for your needs.
The most common blade diameter for table saws is 10 inches. This size is widely used and readily available, making it a popular choice for many woodworkers. A 10-inch blade is suitable for most general-purpose cutting tasks and can handle a wide range of materials, including hardwoods, softwoods, and plywood.
However, if you frequently work with thicker materials or need to make deeper cuts, you may want to consider a larger blade diameter. Blades with a diameter of 12 inches are commonly used for heavy-duty cutting tasks. These larger blades have a greater cutting capacity, allowing you to make deeper cuts and tackle thicker materials with ease.
On the other hand, if you primarily work with smaller stock or require more precise cuts, a smaller blade diameter may be more suitable. Blades with a diameter of 8 inches or less are often used for fine woodworking projects that require intricate and accurate cutting. These smaller blades are also beneficial for minimizing waste and conserving material.
It’s important to note that the size of the blade should match the arbor size of your table saw. The arbor is the shaft on which the blade is mounted, and it is crucial to ensure that the blade you choose is compatible with your saw’s arbor size.
In conclusion, choosing the right blade size for your table saw is essential for achieving optimal performance and results. Consider the type of materials you work with, the depth of cuts you need to make, and the level of precision required for your projects. By selecting the appropriate blade diameter, you can enhance the versatility of your table saw and improve the quality of your woodworking projects.









